In the symphony of Mother Nature’s works, trees and shrubs are beautiful sculptures that adorn our landscape with their inherent beauty. However, they require the love and care a work of art needs to be completely capable. Let’s begin by admiring the realm of Pruning, an ancient horticultural technique that enables us to discover its secrets for generating, enhancing, and renewing such magnificent botanical works.
❓ What is Pruning
Pruning is removing or trimming trees, shrubs, and other plants to remove dead or damaged branches, improve shape, and promote healthy growth. It aids in creating new growth, flowers or fruits and helps maintain the plant’s size, shape, and overall health. Pruning must be performed correctly to avoid damage, ensure plants’ longevity, and maintain vitality.
🌲🌳🌴 Pruning trees, shrubs and bushes
Pruning trees, shrubs, and bushes is the practice of removing dead ends, like woody parts of trees, and extra growth of trees and bushes to enhance their shape, give them a proper appearance and promote productivity. It helps in adequate growth, fruit production and prevents possible health risks.
Pruning of trees would involve selective removal of old dead branches or various parts of trees to improve their appearance and health and enhance fruit production.
Pruning of shrubs and bushes is similar to that of trees, but at a much smaller scale also includes cutting off dead or damaged parts to maintain its shape, aesthetic appeal and well-being. Different types of shrubs require different methods of Pruning.
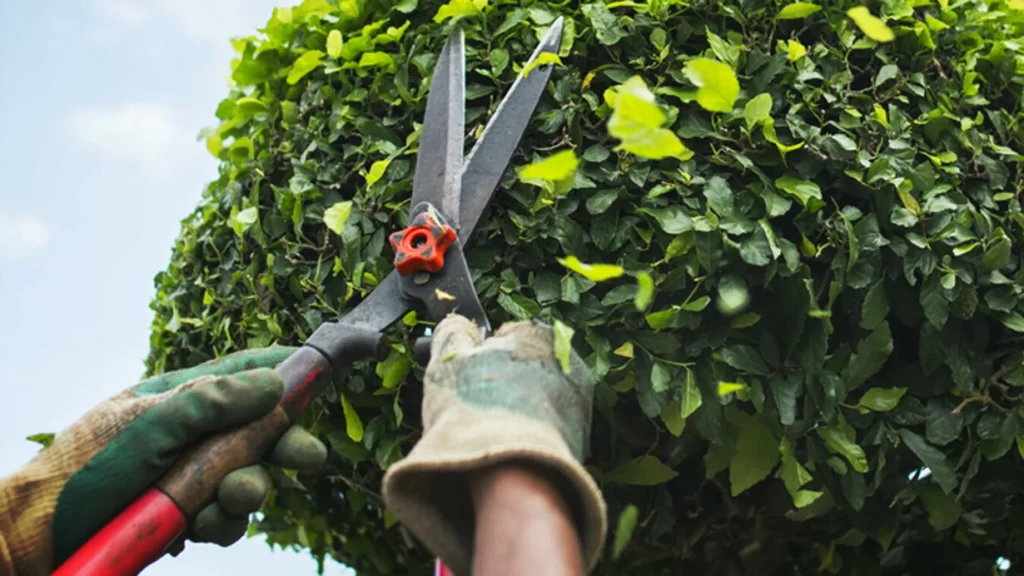

🌺 Pruning flowers
Pruning flowers is not the same as pruning trees, shrubs or bushes, as it involves deadheading of the blooms, which is the removal of faded flowers; pruning dead flowers encourages new flower production and helps the plant conserve its energy and redirects it in the production of new flowers.
Cutting off the old stems in the early spring before the new growth season starts proves beneficial for the flowering plants as they bloom better; different flowering plants require different practices.
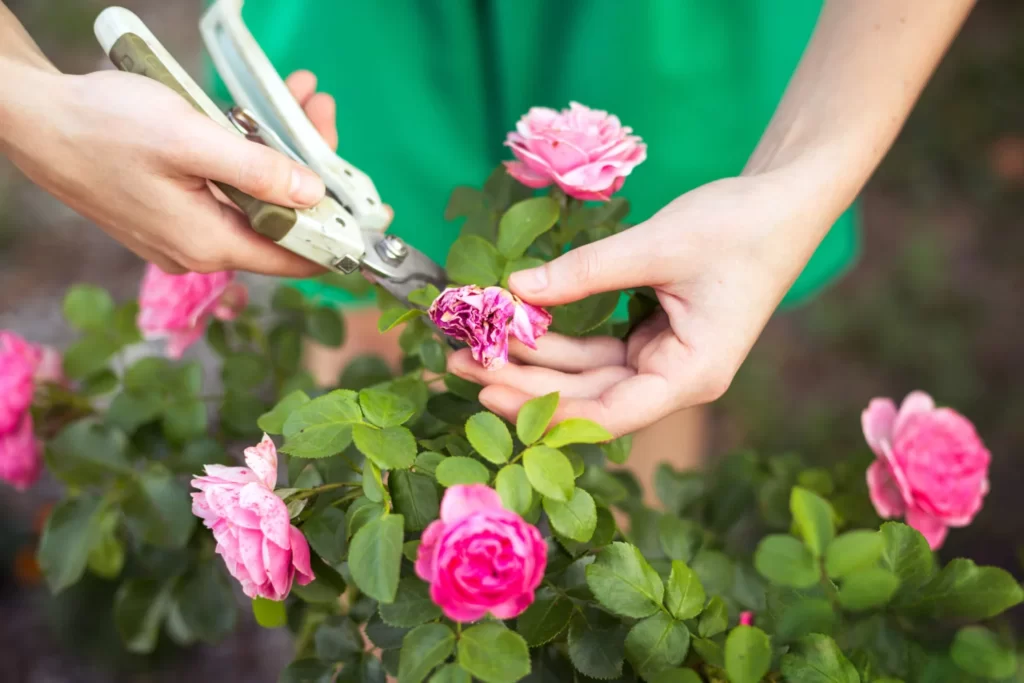

🍂 Burning bush pruning
The burning bush is a species of shrub considered invasive in some regions; it has bright red leaves in autumn. Hence it becomes an excellent choice for landscaping. It’s pruned to control its size, remove the dead or diseased portions, maintain wellness and enhance appearance; it’s pruned around late winter or early spring before the next growing season.

🔡 Types of Pruning
1️⃣ Crown thinning
As part of a particular pruning technique called “crown thinning,” core branches and leaves from a tree or shrub’s crown are removed with care. Crown thinning aims to keep the crown’s natural shape while reducing the crown’s total density. This technique improves air circulation, lightens the load on branches, and allows more sunshine to enter the canopy.
During crown thinning, branches are carefully removed, usually focusing on weak, dead, crossing, or crowded limbs. Thinning the crown can enhance the visual appeal of the tree or shrub overall, encourage healthy development, and lower the danger of disease and pests.
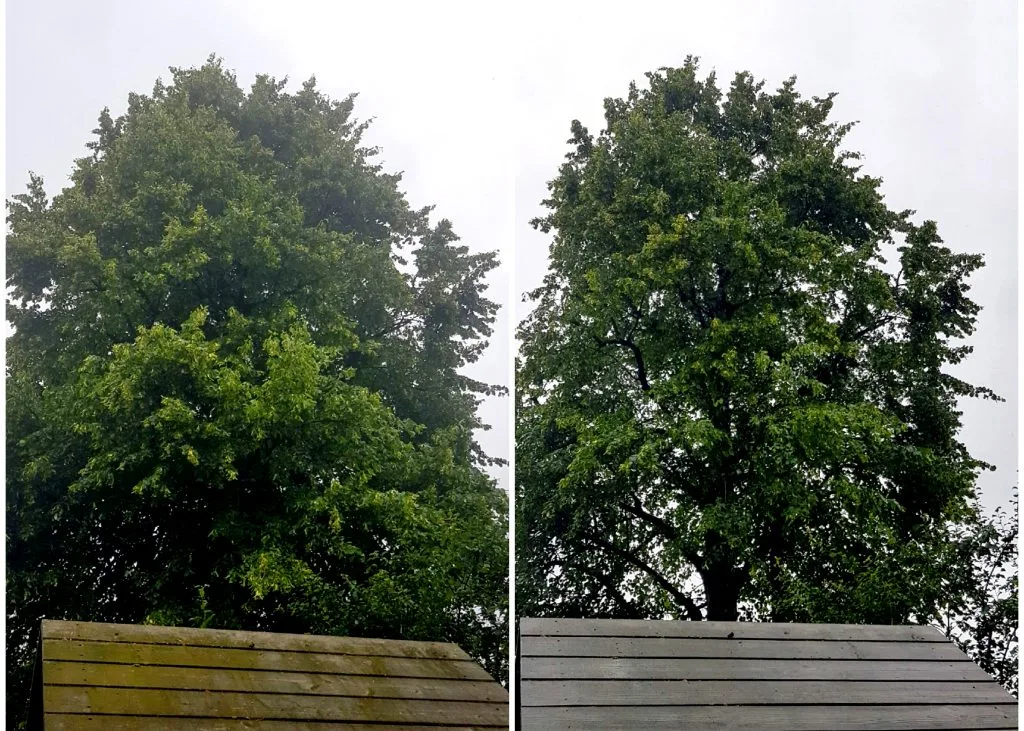

2️⃣ Crown lifting
Crown lifting is a pruning technique that peels off the lower branches to create space between the ground and the lower bottom of the plants; it’s most commonly done to plants around public areas to create a cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing appearance.
While practicing this method, it’s essential to remember not to remove excessive branches as they may affect the stability and grip of the plant.
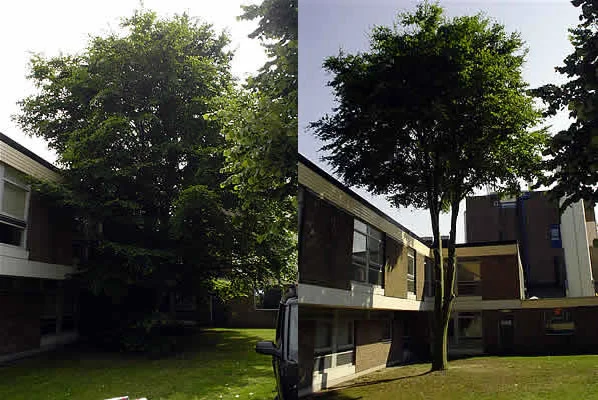

3️⃣ Crown reduction
It’s a technique used to reduce the height of a tree’s canopy by carefully cutting off branches from the top; this helps keep in check the height and disperse of trees or other more diminutive plants and helps maintain their shape and proportions.
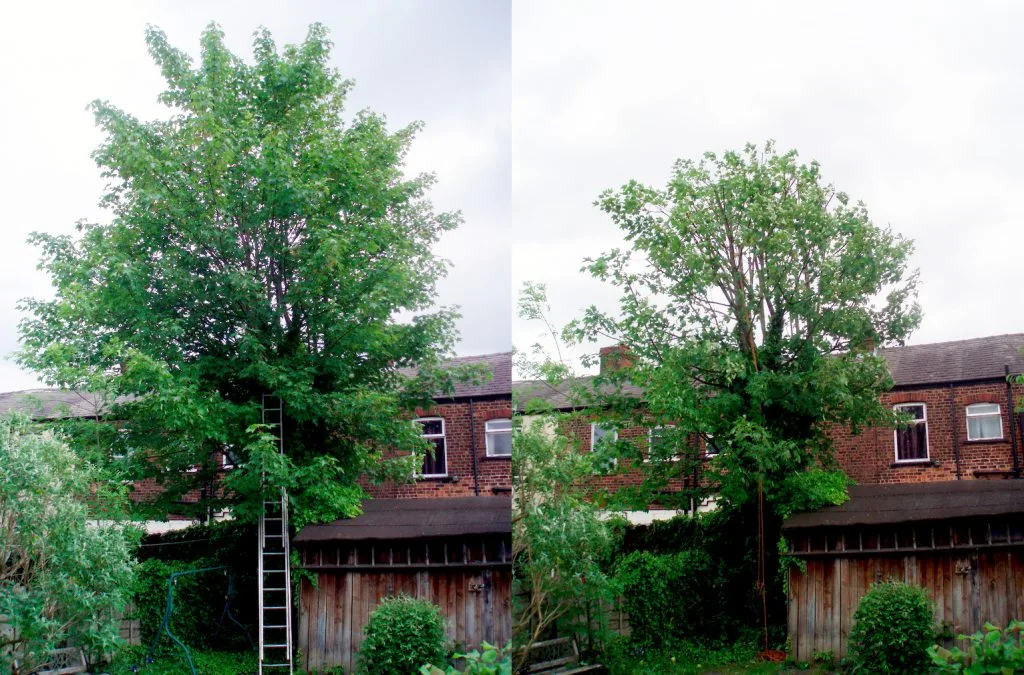

4️⃣ Dead Pruning
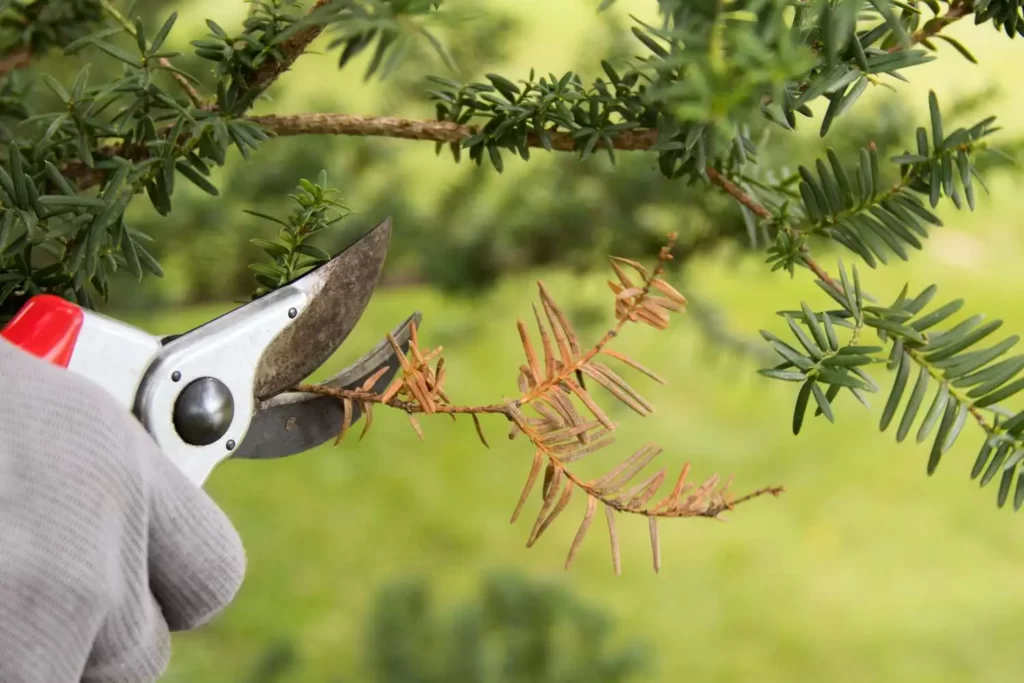
The action of removing dead, decaying or diseased parts from plants or trees is called dead Pruning; it is also known as deadheading or deadwood pruning; leaving dead elements as it is on plants could pose serious harm to them and prevent their growth and development also the risk of the infections spreading to other parts remains concerning if any part is affected by microbes.

5️⃣ Pollarding
A pruning technique that involves cutting off upper branches, excluding the lower branches, is employed at an early stage of the plant and is performed regularly throughout its life; it involves removing all the primary branches and leaving the secondary branches as it is along the lead stem.
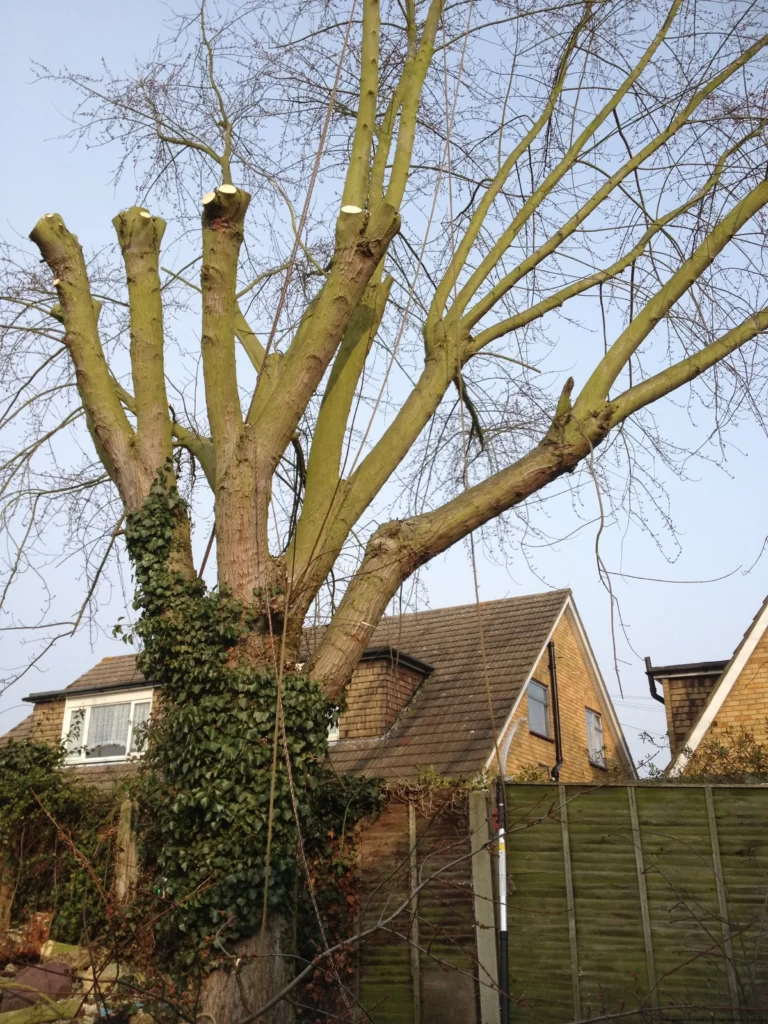

🛠️ Equipment required for Pruning
Here is a list of equipment that you would require:
🥽 Safety glasses
Safety comes first; make sure to have a pair of safety glasses to protect your eyes from all the flying debris while chopping off dead parts.

🪜 Ladder/stool
Keep a small stool or ladder for reaching the higher branches. If you are into vertical landscaping, then you definitely need it.
🧤 Pruning gloves
protect yourselves from thrones and random scratches by wearing pruning gloves.

🧴 Disinfectant
A bottle of disinfectant will clean up your equipment and prevent infection from spreading to other parts of your plant.
✂️ Hand pruners
hand pruners are used to cut off small branches like scissors and offer a good grip and clean cut.
✂️ Needle nose pruners
they are used to get into smaller spaces and are a lead or two; they are mainly employed for cutting green stems or deadheading flowers.

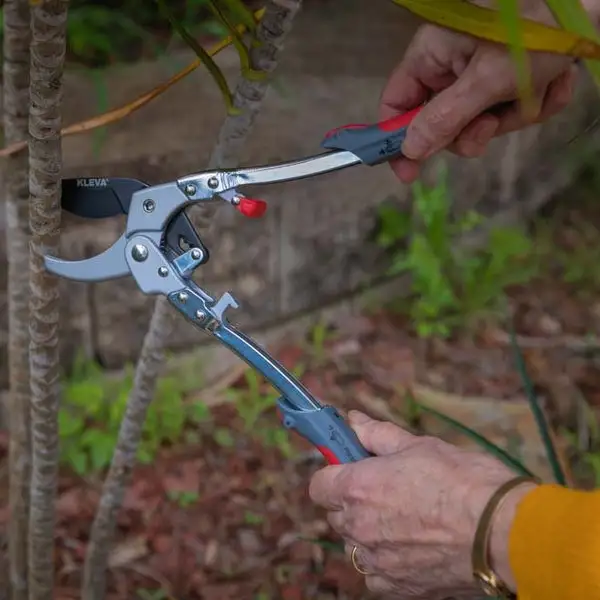
✂️ Looper
Loopers are just like hand pruners but are much more robust and have longer handles; they are used to cut thicker branches, making cutting the more challenging woody parts effortless.

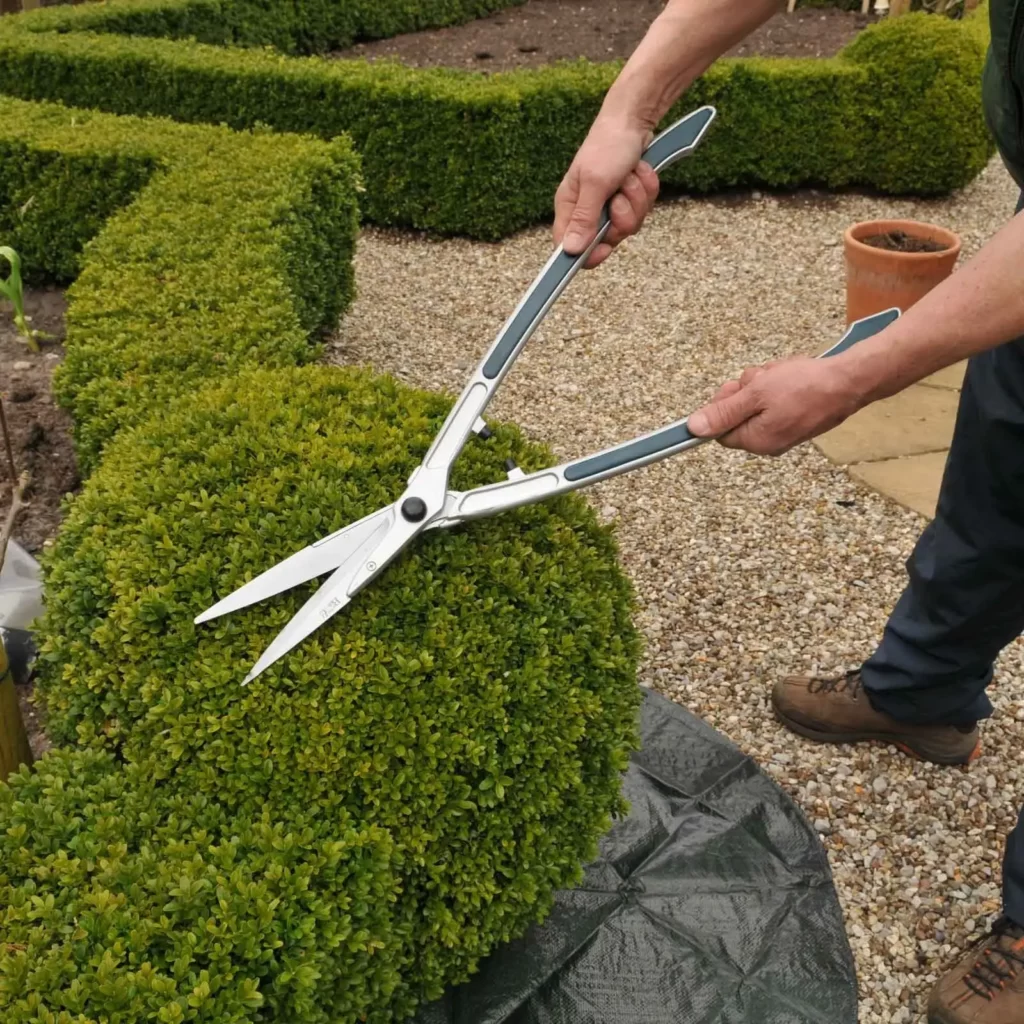
✂ Hedge shears
hedge shears are used to cut several stems at once, reducing effort and time, but they should be used for something other than precision pruning as they cut off leaves or soft branches in bulk.

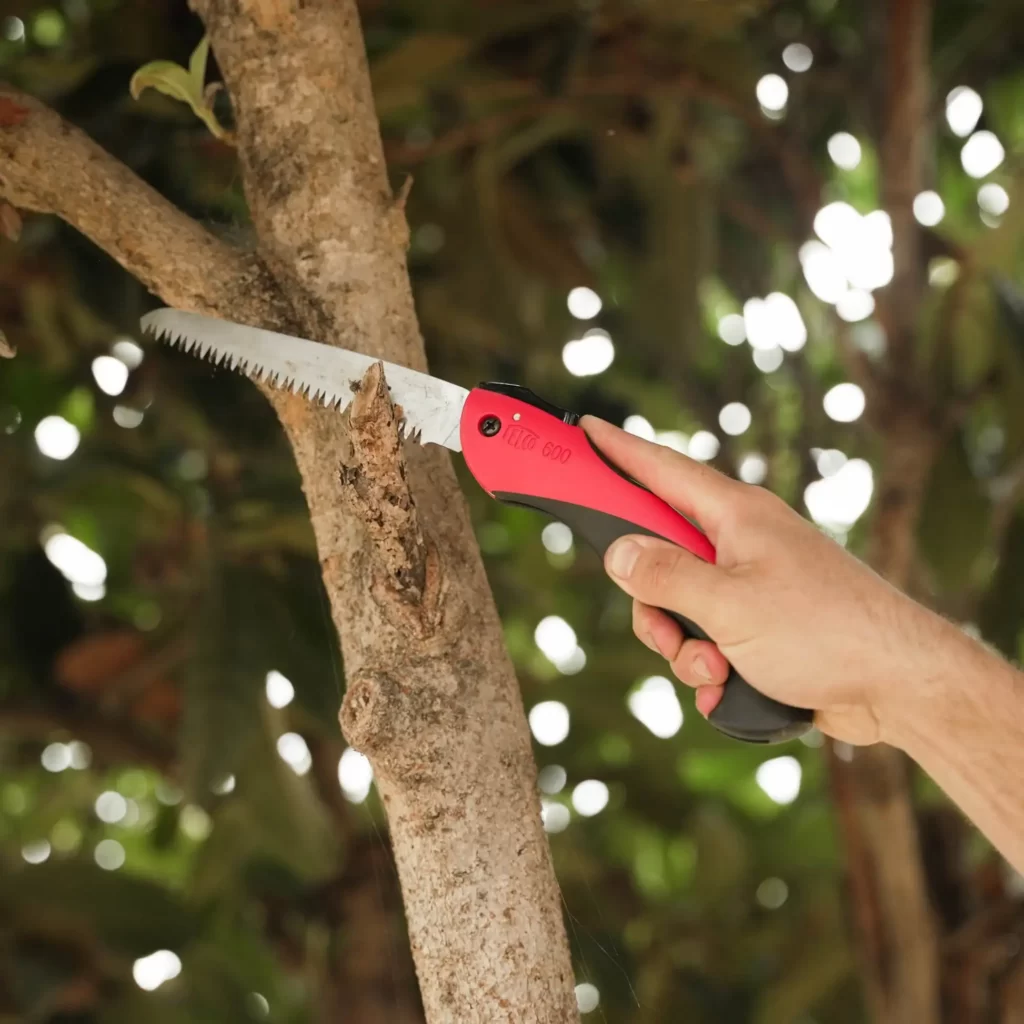
🪚 Pruning saw
Pruning saws are used to chop off much thicker branches or stems.

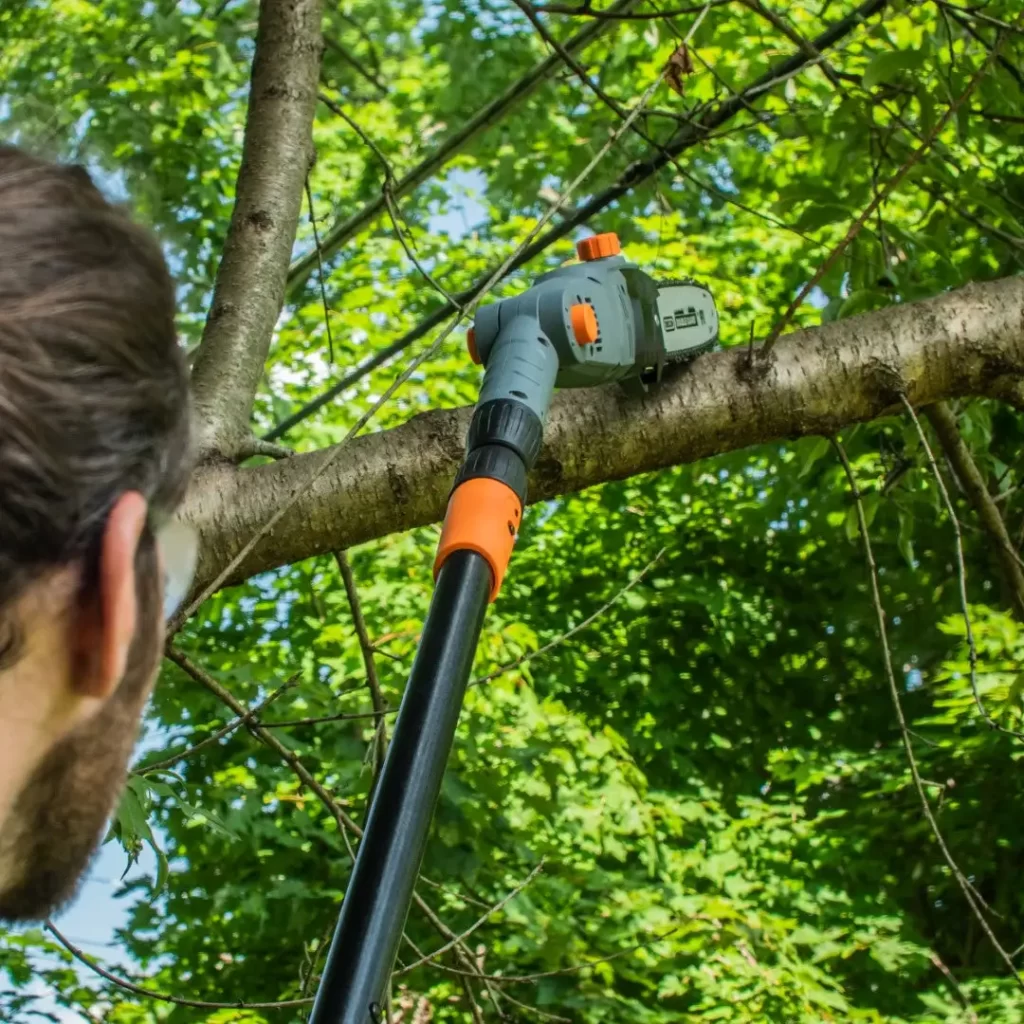
🪓 Pole saw
If you have trees in your garden, consider purchasing a pole saw; these are electric-powered and help reach-prune branches and pruning them.

👨🌾🌳✂️☘️ How to prune plants?
-> Pruning trees
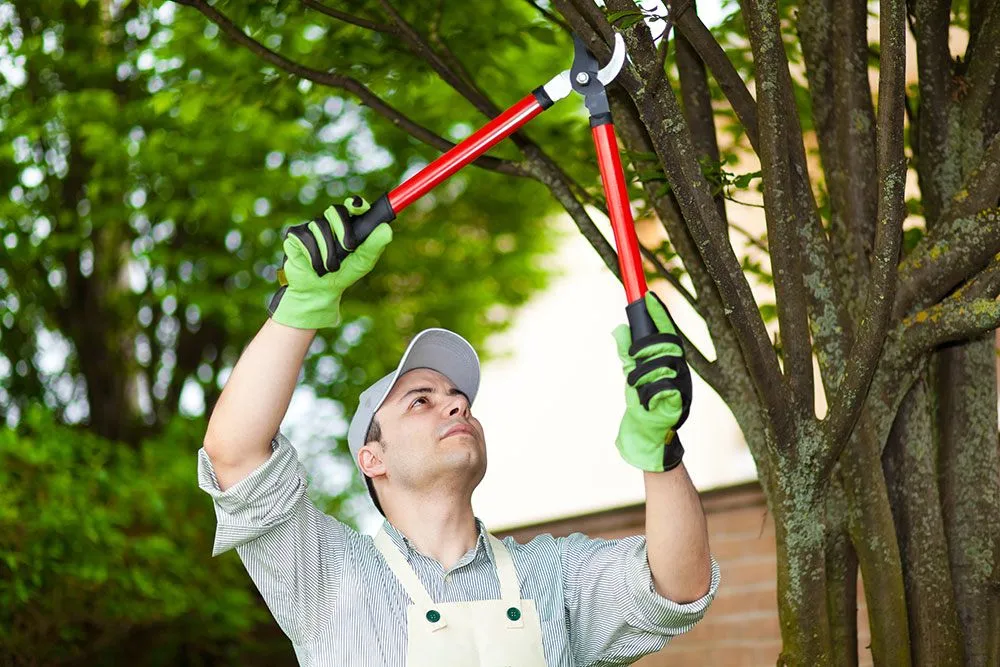
Pruning trees should be performed with proper planning and methods to ensure they are adequately pruned and maintain a great appearance and aesthetics.
Assessing its spread, dead or decaying branches and out-crossed branches is essential to prune a tree.
Firstly, disinfect all the tools so that the infection doesn’t spread to other regions and start with cutting damaged parts which might be infected or dead; removing such parts helps maintain their health and well-being, and remove the parts that are crossing or rubbing over each other, remove the parts growing towards unfavourable directions.
Remember not to trim off more than 25 percent of the foliage and do the Pruning in the dormant season of the plant, during the late fall or early spring; avoid it in the growing season.

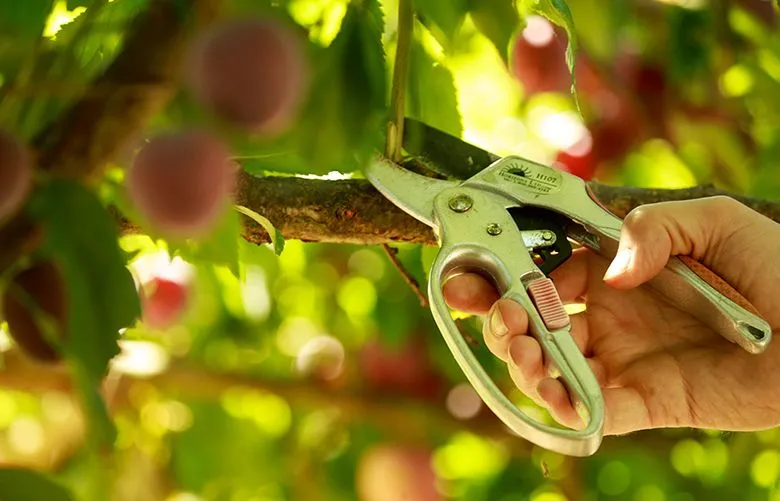
-> Pruning fruit-bearing trees
It’s vital to prune fruit-bearing trees in such a way that it enhances their productivity and health; prune the overly crowded branches to remove the extra weight and allow sunlight and air to penetrate deeper; this way, all the fruits would have almost equal ripening time, assess the type of fruiting tree you have and employ different methods accordingly.
Take care not to prune them during the growing season, trim out excess fruit buds to ensure the production of more significant and high-quality fruits and also reduce the load on fruiting branches; avoid as it may stress the trees and perform regular printing of your fruiting trees to enhance their productivity, maintain shape and health.

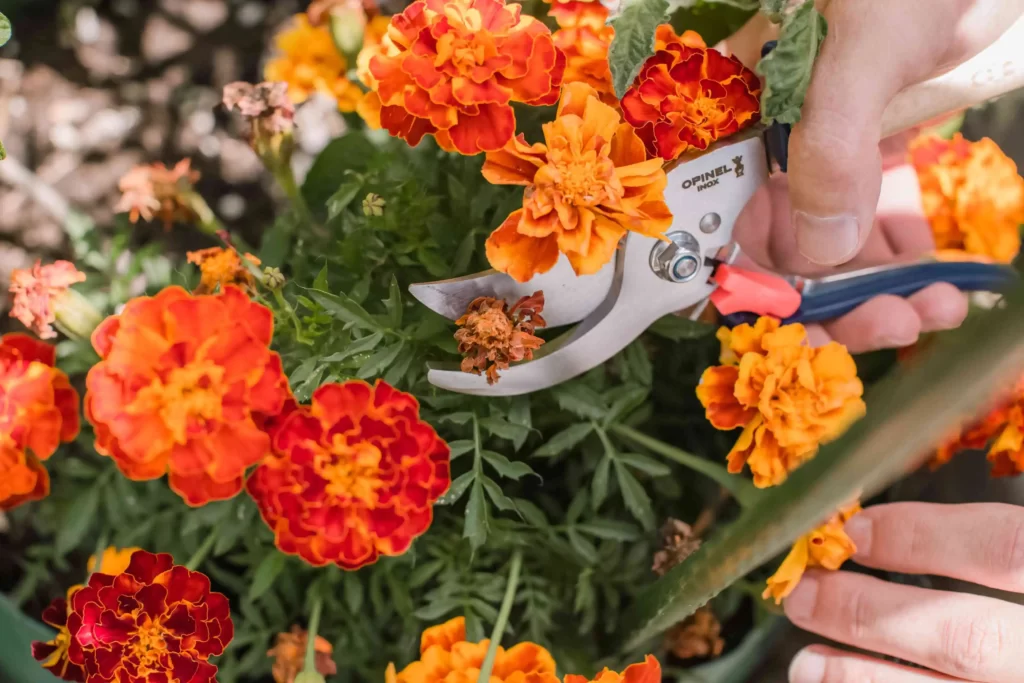
-> Pruning flowers
Identify the needs and the right time for different flowers.
Generally, plants that flower in spring are pruned after they bloom and summer blooming flowers are pruned in the late winters or early spring before new growth begins; remove the dead and diseased parts, overgrown or crossing branches to improve air circulation and sunlight penetration thus enhancing equal blooming of flowers and ensuring their protection from diseases.
To improve flower production, prune around or just above a healthy bud; this redirects the plant’s nutrients toward the newer buds and produces high-quality flowers; regular deadheading of faded flowers encourages the production of newer flowers. Maintain the shape of the flowering plants by cutting off excess flowering branches.

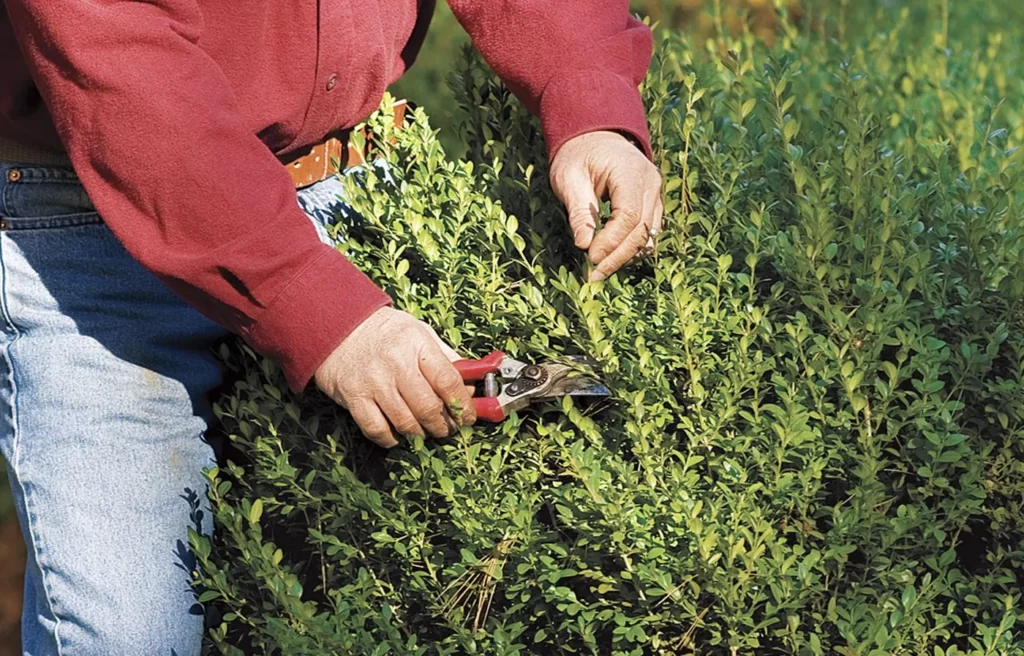
-> Pruning shrubs
Shrubs should be pruned in ways that maintain their shape preventing overcrowding and enhancing visual appeal and wellness; cut out the worn-out branches, properly trim the base for better air circulation, chop off extra growth of branches to give them your desired shape and make cuts above buds angling it away to promote outward growth, avoid cutting off too much of the spread to prevent stressing the plants.

📅 Best time for pruning plants
The best time for pruning different plants depends on their type.
For example, spring flowering plants are pruned after their blooming phase, and summer flowering plants are pruned in late winter or early spring before the new growth session; this promotes new growth and abundant flowering.
Deciduous trees and shrubs are pruned during the late fall to early spring seasons during the plant’s dormant phase, and avoid trimming during summer when they are actively growing.
Evergreen trees or shrubs are also pruned in late winter or early spring.
Prune the flowering shrubs after they bloom and the non-flowering shrubs in late winter/early spring.
Fruiting trees are pruned during late winters to early springs during their dormancy but cutting during freezing periods should be avoided.
Perennials are trimmed during late fall or early spring, and conifers are pruned during late winter or early spring before the next growing season.
🥰 Benefits
- Better health: Eliminating damaged, diseased, or dead branches allows the plant to focus on promoting robust, healthy development.
- Improving Shape and Form: Shaping helps maintain a pleasing structure and contour, improving the plant’s overall aesthetic appeal.
- Optimizing Air Circulation: By thinning out dense foliage, you can improve airflow and reduce the risk of fungus infections.
- Increasing Floral and Yield: When dony by an expert, it promotes the growth of more high-quality flowers or fruits.
- Pruning can revitalize wilting plants by promoting new growth and extending their lives.
- Maintaining Plants the Right Size for Their Designated Area: Regular trimming prevents excessive growth and keeps Plants the Right Size for Their Assigned Area.
- Safety: By removing dangerous branches, you reduce the chance that they’ll cause property damage or personal injury.
😯 Pruning Tips and Mistakes to Avoid
For accurate Pruning, start with clean, pointed devices; trim unhealthy or dead branches carefully; Cut above a sound bud in a growth-focused direction. Cut onto crowded or crossed branches to shape the plant.
Pruning too much causes stress and slows growth; Flower loss may result from poor timing; Diseases are spread through unclean tools, and too much leaf removal makes plants weaker. For frost protection, avoid pruning too close to winter. Before Pruning, find out what the plant requires to avoid mistakes.
🤔 FAQs
How long do pine branches last after the cut?

Under ideal circumstances, you can typically count on chopped pine branches to last a week to a few weeks. Water misting the branches frequently can help keep them fresher, longer. Watch the needles; if they begin to turn brown and fall off, the branches are drying out and losing some of their ornamental appeal.
How to trim leaves during the flowering stage
It can be accomplished by redirecting energy away from the development of buds and toward the trimming of leaves during the flowering phase, but take care because leaves are just as essential for photosynthesis. Avoid overly stressing the plant by strategically trimming.
Can you trim yew in summer?

Since yew shrubs are actively growing in the summer, it’s generally encouraged to avoid excessive Pruning during this time. Yews should be pruned in late the cold or early spring to ensure a speedy regrowth. Major Pruning should wait till the dormant season, but little cutting can be done in the summer.
What Canadian perennials not to cut back in fall
A few perennials which should not be cut during the fall include Sedums, Butterfly Bushes, Coneflowers, Black-Eyed Susans, and Ornamental Grasses.
Is July too late to prune lilacs?

Lilacs should be pruned as soon as the flowering season ends, often in late spring to early summer. Lilacs set their blossoming buds for the following year immediately after flowering, so if you prune them in July, you risk eliminating those for the current year. It is typically advised to avoid pruning lilacs in July to guarantee a beautiful show of its blossoms during the following flowering season.
✅ Conclusion
Trees and bushes are the landscape’s artists and require maintenance equivalent to creating art. An age-old method called Pruning teaches how to create, improve, and renew floral wonders.
Trimming is used in Pruning to eliminate dead tissue, enhance form, and promote growth. It upholds plant size, promotes fruit or flower production, and maintains plant health.
Don’t over-prune, make shoddy cuts, use dirty equipment, remove a lot of foliage, ignore natural form, prune at the wrong time of year, or investigate the plant’s demands.
Different pruning techniques, including crown thinning, raising, reduction, and others, improve the health and appearance of plants.
Pruners, saws, and gloves are helpful tools in the process. Pruning properly will improve a plant’s health, appearance, and longevity.