Tall fescue is a cool-season grass that was introduced in the US and Canada in the 1800s. This grass type grows in bunches and forms a tight sod, and grows well in humid and temperate regions, making it a popular choice for homeowners interested in effective tall fescue grass care.
Tall fescue is popular due to its tolerance of heat, shade, and disease (compared with other cool-season grasses). Its long roots help with better drought resistance. It can grow and thrive in wide-ranging climates, and these tall fescue characteristics make it a reliable choice for many lawns.
Tall fescue requires less watering than Kentucky bluegrass (about 1 inch per week) and can handle foot and pet traffic well.
How to identify Tall fescue grass
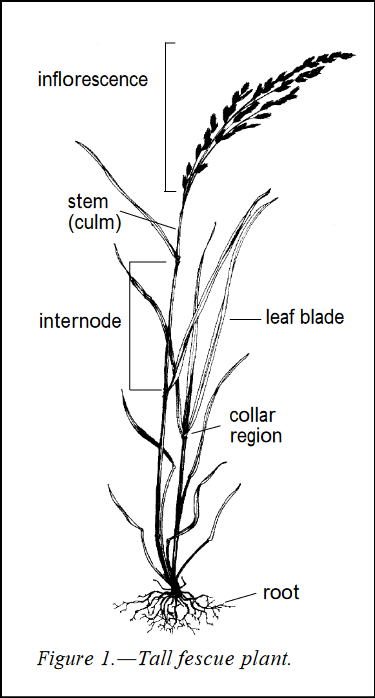
The leaves are green with glossy back surfaces. The leaves are rolled in the bud.
Tall fescue always grows in bunches, with hollow stems and a stem base.

If you look closely at the leaves, you can see clear veins along the length of the leaves.

Tall Fescue Varieties
| Tall fescue variety | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Falcon IV | Better heat and disease resistance |
| Renegade DT | More dense, dwarf, dark green |
| Houndog | Thick, deep, and dense roots |
| Bonfire | Semi-dwarf, suitable for use in sun or partial shade |
| Rebel | Thick, deep and dense roots |
| Kentucky 31 (aka KY 31) | Drought tolerance and persistence. |
| Kentucky 32 tall fescue | Endophyte-free, suitable for forage and animals (horses) |
Some other varieties include Agressor, Bullseye, Fat Cat, Foxhound, Tomcat, Olympic, and Alta tall fescues.
Quick Facts about Tall Fescue
| Characteristic | Facts |
|---|---|
| Other names | Bunchgrass, Reed fescue, Randall, Evergreen |
| Type | Cool season grass |
| Cold tolerance | High |
| Heat tolerance | Moderate |
| Mowing height | 2 to 3 inches |
| Grows up to | 70 inches tall |
| USDA zones | 3 to 8 |
| Native or non-native | Non-native |
| Lifespan | Perennial (Year-round) |
| Thatch formation | Low thatch formation |
| Scientific name | Festuca arundinacea Schreb |
| Foot traffic tolerant | Yes |
| Dog traffic tolerant | Yes |
| Germination from seed | 2 weeks |
| Can be grown by | Seeding, sodding |
| Soil requirements | Slightly acidic |
| Water requirements | High |
| Shade tolerance | Moderate (better than Kentucky Bluegrass) |
| Drought tolerance | Moderate |
| Growth months | Spring and fall |

Soil Requirements
Tall fescue grows best in moist soils with organic matter.
It is resilient and can grow in pH 4.7 – 9.5. It thrives in 5.5 to 7.5 pH.
If your soil’s pH is low, do a lime treatment. If it is high, then use sulfur.
This grass does best in clayey soil. This is because the grass has a long root system which allows it to suck water and nutrients from the soil that can hold more water and nutrients in it. Using the right tall fescue fertilizer further enhances its ability to thrive in such soil conditions.
If your soil is too high in clay, spread some topsoil with compost and organic matter.
Planting Tall Fescue
Spring is the best season if you are planting this grass for the first time. However, you can also plant it in the fall if needed, especially when following a proper tall fescue fertilizer schedule to support healthy growth.
Seeding is the best way to plant it as turf because it germinates quickly and doesn’t require high maintenance when growing for the first time, making it an excellent option for beginners interested in simple tall fescue lawn care.
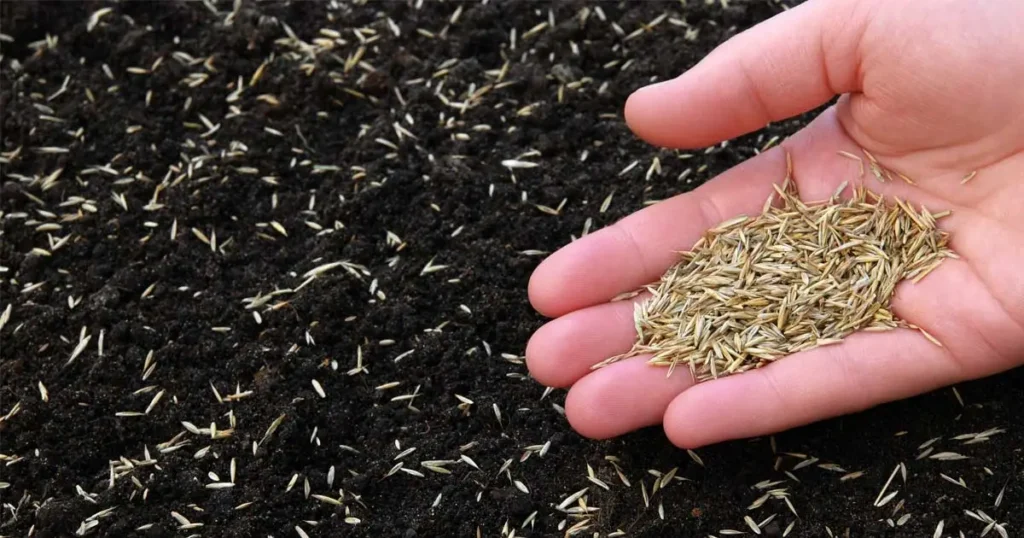

Seed in at a depth of 0.5 inches in the soil. You will need 6-7 pounds per 1000 square feet. Seed only when the soil is dry and water 5 inches after seeding (not all at once). You mustn’t allow the soil to be dry after you’ve seeded the grass, as consistent moisture is a key part of tall fescue grass care.
When planting this grass for the first time, the soil is about 4-5 inches deep.
Water requirements
Thanks to its deep root system, tall fescue requires less frequent watering. Therefore, you do not need to water your lawn daily, and resources on topics like lawn care or landscaping website design often highlight this water-saving benefit.

You should be good at watering only once or twice a week.
When do I water my lawn?
Do not water your tall fescue until you you see signs of wilting or rolling leaves.
The only thing to remember here is that grass requires frequent watering this incredible season—not that you have to water every day, but you need water to percolate well into the soil. Proper irrigation is one of the key tall fescue characteristics that supports healthy growth.
So if your water runs off during grass irrigation, you need to wait for the water to seep into the soil, which is such soil that it can hold enough water during summer. Understanding tall fescue pros and cons can also help you manage watering practices more effectively.
Mowing requirements
It is best to mow tall fescue, 2 to 3 inches high. If you mow lower, your grass may be dominated by other weeds and grass types, so pairing proper mowing with the right tall fescue fertilizer will help maintain a healthy, thick lawn.
You need sharp blades; do not mow when the grass is wet. Knowing mowing best practices is just as important as learning how to plant fescue grass seed for a healthy lawn.
To make it heat resistant in the summer, keep it at least 3 inches tall. Also, mow only once a week, and combine this practice with a consistent tall fescue fertilizer schedule to ensure strong growth.
During spring, mowing twice weekly and keeping the height between 2 and 2.5 inches is advisable. This routine is an important part of effective tall fescue lawn care to keep your turf healthy and dense.
Mowing height also depends on the variety that you are planting. Creeping red fescue can handle 2 inches, but Kentucky-32 should be mowed to 3 inches.
Remember that this grass grows through its crow,n which is delicate and essential for grass to grow, so do not mow too low that you scalp your grass.

If you mow regularly, you do not need to collect grass clippings. But if you mow infrequently (and do not maintain the 1/3 rule of mowing), you need to collect the clippings to avoid thatch buildup.
Fertilizer requirements
It is best to fertilize tall fescue with 3 pounds of nitrogen per 1000 square feet a year.
If your soil is clayey, it can do well with just 2 applications per year. If your soil is more sand than clay, you’d need 3 fertilizer applications yearly.
If you’re applying a slow-release nitrogen:
Apply 3 pounds per 1000 square feet in September only.
If you’re using water-soluble nitrogen:
In September and November, apply 1 pound per 1000 square feet, and apply 0.5 pounds in February and March.
Mixing with other grasses
Tall fescue is generally mixed with perennial ryegrass, orchardgrass,
Diseases, Weeds and Pest problems
Diseases
The most common diseases that plague tall fescue are caused by fungus. Crown rust, Stem rust, brown patch (east US), fusarium patch, and net blotch.
Crown rust (caused by Puccinia coronata) occurs during moist and warm periods, generally in July.
Fusarium blight causes problems in newly planted lawns, while brown patches commonly occur on older lawns, as the grass does not last much longer than other winter grasses.
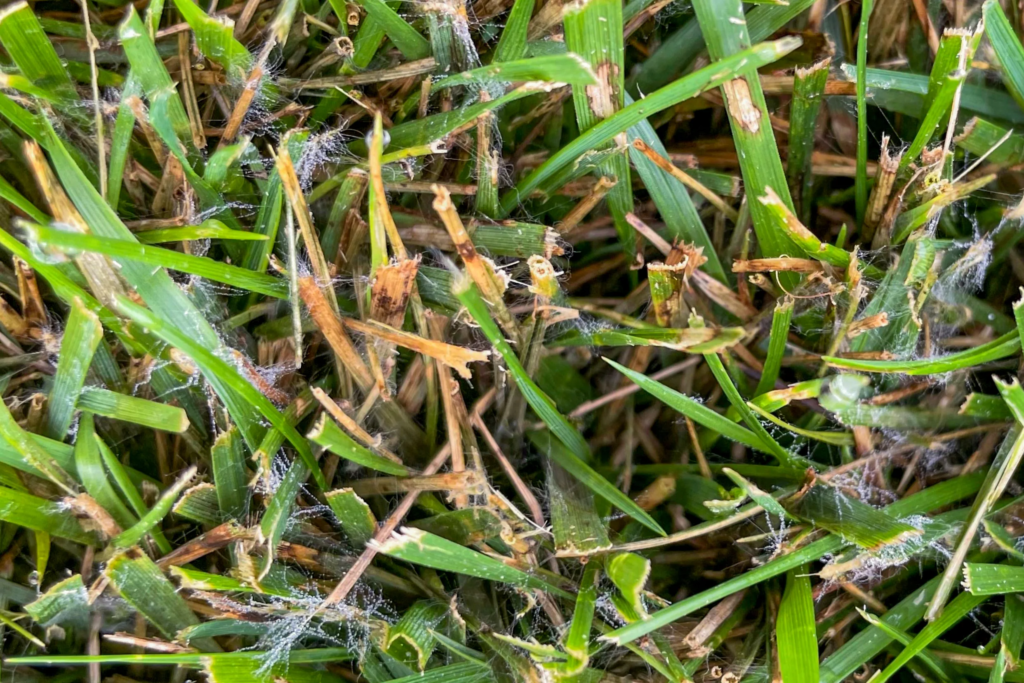

Insects and pests
The most common threats include cutworms, white grubs, Masked chafers, Japanese beetles, and June beetles (Junebugs).
When do I treat for White Grubs?
When you see more than 3 white grubs in a square foot (tested randomly at 3 places), when you need to treat white grubs. Apply carbaryl or Triclorfon to treat.
Weeds
Most weed threats include broadleaf weeds such as dandelion, plantain, and crabgrass.
To prevent weeds in your lawn, keep your tall fescue as dense as possible and within the recommended heights of 2-3 inches.
FAQs
Is Tall fescue good for the environment?
Turf-type tall fescue with endophyte (E+) is disease-resistant but harmful to livestock and nonsustainable for the environment. In the United States, 80% of this type of grass is endophytic. Understanding tall fescue pros and cons helps homeowners make informed decisions.
Which zone is tall fescue best suited for?
Tall fescue is best suited for the transition zone. Warm-season grasses like Bermuda and Zoysia don’t handle cold well. One of the key tall fescue characteristics is its ability to adapt to both warm and cool conditions.
Is Kentucky 31 the same as Kentucky bluegrass?
Kentucky 31, or KY-31, is a persistent and drought-tolerant variety of tall fescue grass. Kentucky bluegrass, also a cool-season grass, has different varieties, but none are called Kentucky 31. When comparing, consider tall fescue lawn care needs versus those of Kentucky bluegrass.
How do you plant tall fescue grass seed?
To get the best results, prepare the soil properly, loosen the top layer, and ensure even seeding. Water lightly but consistently after planting. Following best practices on how to plant fescue grass seed ensures healthy growth and long-lasting turf.
What is the best tall fescue fertilizer schedule?
A balanced tall fescue fertilizer schedule usually involves feeding in early spring, late summer, and fall. Pairing this with proper mowing height and watering routines enhances overall tall fescue grass care and supports long-term lawn health.
Maintenance Calendar with activities for KBG
March, April, May
Mowing
Maintain a recommended height of 2-3 inches.
Watering
Water 1 inch per week, ideally not all at once. Water regularly with 0.33 inches 3 times in a week.
Overseeding
Overseed to make your tall fescue look dense.
Weed control
Apply a crabgrass weed control (pre-emergent such as Dimension). If you’ve just seeded or overseeded, skip the pre-emergent.
June, July and August
Mowing
Mow to 2-3 inches.
Watering
Water 1 inch per week. This includes rainfall, so adjust accordingly.
Pest control
Treat with insecticide.
September, October and November
Mowing
Mow to maintain a height of 2-3 inches.
Watering
You will need only 0.5 inches of water per week.
Overseeding
As tall fescue becomes weaker during the summer, it is necessary to overseed it in the fall. Apply fertilizer, rake clippings and mow low when overseeding tall fescue grass.
Fertilization
Apply nitrogen in the fall to encourage thicker and more resilient stands with a jump-start for spring growth.
December, January and February
Mowing
Mow only if needed to 3-4 inches.
Winter flush
Check for de-icing salt damage and flush with water.
Latest research into Kentucky bluegrass
References
- Hannaway, D., Fransen, S., Cropper, J., Teel, M., Chaney, M., Griggs, T., Halse, R., Hart, J., Cheeke, P., Hansen, D., Klinger, R., & Lane, W. (1999). Tall Fescue. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/David-Hannaway/publication/45793997_Tall_fescue_Festuca_arundinacea_Schreb/links/00b7d5311e9fbd435e000000/Tall-fescue-Festuca-arundinacea-Schreb.pdf
- Tall Fescue. (n.d.). https://dlf.com/seeds/sport-landscape/species-and-varieties/tall-fescue?PageSize=36&RequestType=UpdateList
- Tall Fescue. (n.d.). https://aggie-hort.tamu.edu/plantanswers/turf/publications/tallfesc.html
- Erin Hill and Kevin Frank, Michigan State University Department of Plant, Soil and Microbial Sciences. (2023, May 23). Pain in the grass: Tall fescue. Plant & Pest Diagnostics. https://www.canr.msu.edu/news/pain-in-the-grass-tall-fescue
- Best mowing Practices for fescue grass lawns. (n.d.). https://www.outsidepride.com/seed/grass-seed/fescue-grass-seed/mowing-fescue-grass/
- Cowan, J. R. (1956). Tall Fescue. Advances in Agronomy, 283–320. doi:10.1016/s0065-2113(08)60692-6
- USDA NRCS National Plant Data Center, & Darbyshire, S. J., J. (1989). Plant Guide. https://plants.usda.gov/DocumentLibrary/plantguide/pdf/pg_loar10.pdf